17 Pigmented lesions: Malignant melanoma
Figure 17.1 Melanoma.
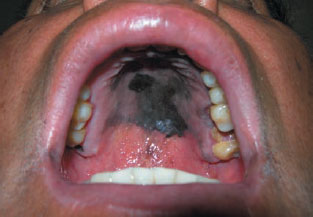
Figure 17.2a Melanoma; testing with cotton pledget.
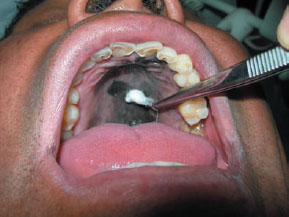
Figure 17.2b Melanoma; cotton is stained.
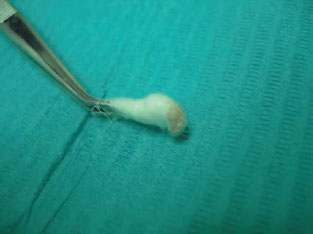
Figure 17.3 Melanoma 10 ×.
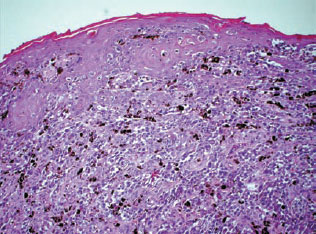
Definition: Malignant neoplasm of melanocytes.
Prevalence (approximate): Uncommon – probably 1.2 cases per 10 million population per year. Japan and Uganda are areas of higher prevalence. Oral melanoma accounts for 0.2–8% of melanomas and approximately 1.6% of all head and neck malignancies. The oral mucosa is primarily involved in less than 1% of melanomas.
Age mainly affected: Middle-aged and older.
Gender mainly affected: M > F.
Etiopathogenesis: Sunlight exposure is causal in skin melanomas, which have increased in almost epidemic fashion over the past decades, especially in fair-skinned peoples. The cause of oral melanoma, however, is unknown and no link has been established with chemical or physical trauma, tobacco use, betel chewing or oral hygiene. Most oral melanomas are thought to arise de novo. Though oral nevi are potential sources of some melanomas they are usually benign. Even blue nevi, which are more common on the palate – the site of predilection for melanoma – rarely undergo malignant transformation.
Diagnostic features
History: Melanomas are usually symptomless in early stages; later swelling, tooth mobility, or bleeding may appear.
Clinical features
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


