Q. 2. Corticosteroids in dentistry.
Ans. Corticosteroids are the hormones produced by the cortex of the adrenal gland. They are as follows:
The secretion of adrenal cortex is under the control of ACTH secreted by the anterior pituitary, which in turn is regulated by corticotropin releasing factor (CRF). This is termed as hypothalamic−pituitary−adrenal axis.
Classification of corticosteroids
Mechanism of action
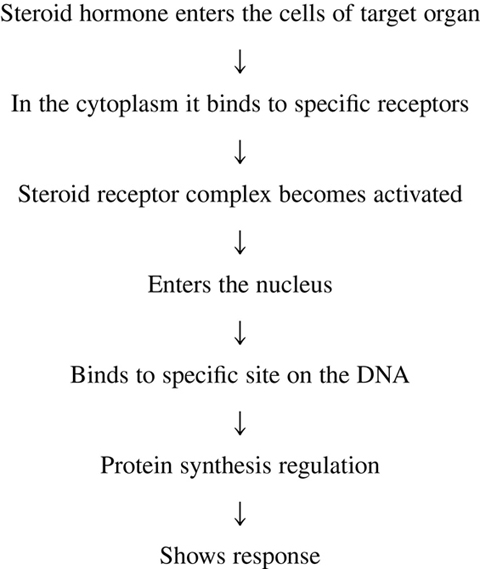
Corticosteroids bind to specific receptors in the cytoplasm, the drug−receptor complex is transported into the nucleus where it binds to specific sites on DNA and regulates the synthesis of new proteins that bring about the hormone effects.
I. Prednisolone
• It is more selective glucocorticoid and is four times more potent than hydrocortisone.
• Used for allergic, inflammatory, autoimmune diseases and in malignancies.
• For example, available as DELTACORTRIL, HOSTACORTIN-H,5,10 mg tab, 20 mg/mL for i.m., intraarticular injection, WYSOLONE, NUCORT, 5, 10, and 20 mg tab.
II. Methylprednisolone
III. Triamcinolone
• Slightly more potent but highly selective glucocorticoid than prednisolone: 4−32 mg/day oral, 5−40 mg i.m., intraarticular injection. Also used topically.
• For example, available as KENACORT, TRICORT 1, 4 and 8 mg tab., 10 mg/mL, 40 mg/ml (as acetonide) for i.m., intraarticular injection LEDERCORT 4 mg tab.
IV. Dexamethasone
• Very potent and highly selective glucocorticoid than prednisolone. It is used for inflammatory and allergic conditions in a dose of 0.5–5 mg/day oral. In shock, cerebral oedema, etc. 4−20 mg/day IV, IM, injection. Also used topically.
• For example, available as DECADRON, DEXONA 0.5 mg tab, 4 mg/mL (as sodium phosphate) for IV, IM, injection, 0.5 mL oral drops, etc.
V. Betamethasone
• Same as that of dexamethasone: 0.5–5 mg/day oral, 4−20 mg/day IV, IM, injection or infusion, also topical.
• For example, available as BETNESOL, BETACORTRIL, CELESTONE 0.5 mg, 1 mg tab and 4 mg/mL (as sodium phosphate) for IV, IM, injection, 0.5 mL oral drops, etc.
Most of the adverse effects of glucocorticoids are extension pharmacological actions and are dependent on dose, duration of therapy and the relative potency of additional mineralocorticoid effects.
i. Cushing syndrome: Abnormal fat distribution causes moon face, buffalo hump, truncal obesity, muscle wasting, thinning of limbs and skin, easy brushing, purple striae and acne.
ii. Hyperglycaemia: Precipitation of diabetes mellitus or aggravation of preexisting diabetes.
iii. Susceptibility of infection: Long-term therapy with steroids leads to immunosuppression, which makes the patient more vulnerable to various opportunistic infections like fungal, viral and bacterial, etc.
iv. Osteoporosis: Especially of the vertebrae is more common in the elderly.
v. Avascular necrosis: Avascular necrosis of the bone due to restriction of blood flow through bone capillaries may cause pain and restriction of movement. Growth in children may be suppressed.
vi. Peptic ulceration: This may sometimes occur on prolonged therapy especially when other ulcerogenic drugs are (e.g., NSAIDs) used concurrently.
vii. Mental disturbance: Include euphoria, psychosis and depression.
viii. Eye: Cataract and glaucoma may occur on prolonged therapy.
x. Other effects: Raised intracranial pressure, convulsions, hypercoagulability of the blood and menstrual disorders.
xi. Mineralocorticoid effects: This includes salt and water retention, oedema, hypokalaemia and hypertension are rare with selective glucocorticoids.
xii. Thinning of muscles: Steroid treatment can cause hypokalaemia leading to muscle weakness and fatigability. Long-term steroid therapy leads to steroid myopathy.
xiii. HPA axis suppression: The most undesirable and dangerous outcome of long-term steroid therapy leads HPA axis suppression.
Short essays
Q. 1. Metronidazole.
Ans.
• Metronidazole is a potential agent for local antimicrobial therapy due to its selective antimicrobial features against the obligate anaerobes.
• The most extensively tested and used device for metronidazole application is a gel consisting of a semisolid suspension of 25% metronidazole benzoate in a mixture of glyceryl mono-oleate and sesame oil (Elyzol Dental Gel, Dumex, Copenhagen, Denmark). Applied with a syringe inserted into the pocket, the gel increases in viscosity after placement.
• Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole compound used to treat protozoal infections. It is bactericidal to anaerobic organisms.
Clinical uses
• Although metronidazole is not the drug of choice for treating A. actinomycetemcomitans infections, it may be effective at therapeutic levels because of its hydroxy metabolite. When used in combination with other antibiotics metronidazole is effective against A. actinomycetemcomitans.
• Metronidazole is also effective against anaerobes such as Porphyromonas gingivalis and Prevotella intermedia.
• Metronidazole has been used clinically to treat gingivitis, acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (NUG), chronic periodontitis and aggressive periodontitis.
• A single dose of metronidazole (250 mg orally) appears in both serum and GCF in sufficient quantities to inhibit a wide range of suspected periodontal pathogens.
• Administered systemically (750−1000 mg/day for 2 weeks), metronidazole reduces the growth of anaerobic flora, including spirochetes, and decreases the clinical and histopathologic signs of periodontitis.
• The most common regimen is 250 mg three times daily (t.i.d.) for 7 days.
Subgingival metronidazole
Side-effects
• Metronidazole has an antiabuse effect when alcohol is ingested, resulting in severe cramps, nausea and vomiting. Hence, products containing alcohol should be avoided during therapy and for at least 1 day after therapy is discontinued.
• Metronidazole also inhibits warfarin metabolism. Patients undergoing anticoagulant therapy should avoid metronidazole because it prolongs prothrombin time.
• It also should be avoided in patients who are taking lithium.
Q. 2. Oral penicillin.
Or
Classification and uses of oral penicillins.
Or
Uses and side-effects of oral penicillins.
Ans.
• Antibiotic is a chemical substance produced by a microorganism, which has the capacity to inhibit the growth or kill other organism in dilute solution.
• Penicillin is the most important and the first antibiotic to be used, obtained from a fungus of penicillium notatum, but the yield was very low. The present source of pencillin is the high-yielding P. chrysogenum.
Classification
Natural penicillins
Semisynthetic Penicillins
Therapeutic uses
i. Penicillin G or benzyl penicillin is the drug of choice for infection caused by bacteria susceptible to it, that is Streptococci, Pneumococci, Bacillus anthracis, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Clostridia, Listeria, Spirochetes and Neisseria species.
i. Pharyngitis, otitis media, scarlet fever, rheumatic fever. 0.5−5 MU i.v. 8 hourly for 7−10 days.
ii. Subacute bacterial endocarditic caused by Step. viridans or faecalis. 10−20 MU i.v. daily with streptomycin 0.5 g 1M BD for 2−6 weeks.
i. Penicillins have been taken over by fluoroquinolones/ceftriaxones as the first line drugs. However, it can be used in NPPG infection as 4.8 MU i.m. single dose divided and given in both buttocks or procaine penicillin with Ig probenecid orally.
ii. For ophthalmia neonatorum due to sensitive N. gonorrhoeae.
Or
5 MU i.m. of sodium penicillin G 6 hourly for 2 weeks.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


