P
paclitaxel
(Abraxane, Anzatax[aus], Onxol, Taxol)
Do not confuse paclitaxel with Paxil, or Taxol with Taxotere.
Drug Class:
Serious Reactions
! Neutropenic nadir occurs at approximately day 11 of paclitaxel therapy.
! Anemia and leukopenia are common reactions.
! Thrombocytopenia occurs occasionally.
! A severe hypersensitivity reaction, including dyspnea, severe hypotension, angioedema, and generalized urticaria, occurs rarely.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort if GI side effects occur.
• Patients receiving chemotherapy may require palliative therapy for stomatitis.
• Patients on chronic drug therapy may rarely have symptoms of blood dyscrasias, which can include infection, bleeding, and poor healing.
Drug Class:
Precautions and Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to paliperidone, risperidone, or its components
Drug Interactions of Concern to Dentistry
Serious Reactions
! Prolongation of QT interval may produce torsades de pointes. Patients with bradycardia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia are at increased risk.
! Orthostatic hypotension including dizziness, tachycardia, and syncope with standing may occur.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min before standing to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Assess for presence of extrapyramidal motor symptoms such as tardive dyskinesia and akathisia. Extrapyramidal motor activity may complicate dental treatment.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort if GI side effects occur.
Consultations:
• In a patient with symptoms of blood dyscrasias, request a medical consultation for blood studies and postpone treatment until normal values are reestablished.
• Medical consultation may be required to assess disease control.
• Physician should be informed if significant xerostomic side effects occur (e.g., increased caries, sore tongue, problems eating or swallowing, difficulty wearing prosthesis) so that medication change can be considered.
• Consultation with physician may be necessary if sedation or general anesthesia is required.
Drug Class:
Drug Class:
Bone-resorption inhibitor, electrolyte modifier
Mechanism of Action
A bisphosphate that binds to bone and inhibits osteoclast-mediated calcium resorption.
Serious Reactions
! Hypophosphatemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalcemia occur more frequently with higher dosages.
! Anemia, hypertension, tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, and somnolence occur more frequently with 90-mg doses.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Evaluate patient for signs and symptoms of osteonecrosis of the jaw.
• Determine why patient is taking the drug.
• This drug may be used in the hospital or on an outpatient basis. Confirm the patient’s disease and treatment status.
• Examine for oral manifestation of opportunistic infection.
• Monitor and record vital signs.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort if GI side effects occur.
• Question patient about tolerance of NSAIDs or aspirin related to GI disease.
• Be aware of the oral manifestations of Paget’s disease (macrognathia, alveolar pain).
• Patients may have received other chemotherapy or radiation; confirm medical and drug history.
Drug Class:
Indications and Dosages
Drug Class:
Antineoplastic, monoclonal antibody
Mechanism of Action
Therapeutic Effect: Inhibits growth and survival of selected human tumor cell lines expressing EGFR.
Pharmacokinetics
Half-life: 4–11 days. Other pharmacokinetic parameters have not been clearly established.
Indications and Dosages
Precautions and Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to panitumumab or its components; sunlight may exacerbate skin reactions
Serious Reactions
! Dermatologic toxicities have been reported.
Dental Considerations
Teach Patient/Family to:
• Be aware of oral side effects of drug.
• Report oral lesions, soreness or bleeding to dentist.
• Use effective, atraumatic oral hygiene to minimize soft tissue inflammation.
• Update health and medication history if physician makes any changes in evaluation or drug regimen; include OTC, herbal, and nonherbal drugs in the update.
Drug Class:
Gastrointestinal, proton pump inhibitor
Serious Reactions
Dental Considerations
General:
• Avoid aspirin and NSAIDs for pain control if GI disease requires.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort because of possible regurgitation of stomach contents.
• Patients with gastroesophageal reflux may have oral symptoms, including burning mouth, secondary candidiasis, and dental erosion
Drug Class:
Pharmacokinetics
Protein binding: 90%. Primarily excreted in urine as inactive metabolites. Half-life: Unknown.
Category and Schedule
Pregnancy Risk Category: B (D if used for prolonged periods, high dosages at term)
Drug Class:
Serious Reactions
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


 Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian Cancer Breast Carcinoma
Breast Carcinoma Non–Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma
Non–Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma KS
KS Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
 Renal Impairment
Renal Impairment Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting
Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting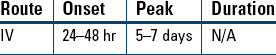
 Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia Paget’s Disease
Paget’s Disease Osteolytic Bone Lesion
Osteolytic Bone Lesion Pancreatic Insufficiency
Pancreatic Insufficiency EGFR-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
EGFR-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Dosing Adjustments
Dosing Adjustments Dermatologic Toxicity
Dermatologic Toxicity
 Erosive Esophagitis
Erosive Esophagitis Hypersecretory Conditions
Hypersecretory Conditions
 Vascular Spasm
Vascular Spasm Antidiarrheal
Antidiarrheal Hypertension
Hypertension