O
octreotide acetate
(Sandostatin, Sandostatin LAR)
Do not confuse octreotide with OctreoScan, or Sandostatin with Sandimmune or Sandoglobulin.
Drug Class:
Secretory inhibitor, growth hormone suppressant
Serious Reactions
! Patients using octreotide may develop cholelithiasis or, with prolonged high dosages, hypothyroidism.
Dental Considerations
General:
• This drug is administered in several disease states; determine patient’s medical and drug history and exact use to accurately plan patient management.
• Monitor and record vital signs.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort if GI side effects occur.
• Question patient about tolerance of NSAIDs or aspirin related to GI disease.
• This drug may be used in the hospital or on an outpatient basis. Confirm the patient’s disease and treatment status.
• Patient may need assistance in getting into and out of dental chair. Adjust chair position for patient comfort.
• Examine for oral manifestation of opportunistic infection.
Teach Patient/Family to:
• Encourage effective oral hygiene to prevent soft tissue inflammation.
• Prevent trauma when using oral hygiene aids.
• Use powered tooth brush if patient has difficulty holding conventional devices.
• Update health and medication history if physician makes any changes in evaluation or drug regimens; include OTC, herbal, and nonherbal drugs in the update.
ofloxacin
(Apo-Oflox[can], Floxin, Floxin Otic, Ocuflox)
Do not confuse Floxin with Flexeril or Flexon, or Ocuflox with Ocufen.
Drug Class:
Serious Reactions
! Antibiotic-associated colitis and other superinfections may occur from altered bacterial balance.
! Hypersensitivity reactions, including photosensitivity (as evidenced by rash, pruritus, blisters, edema, and burning skin), have occurred in patients receiving fluoroquinolones.
! Arthropathy (swelling, pain, and clubbing of fingers and toes, degeneration of stress-bearing portion of a joint) may occur if the drug is given to children.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Because of drug interaction, do not use ingestible sodium bicarbonate products, such as the Prophy-Jet air polishing system, until 2 hr after drug use.
• Examine for oral manifestation of opportunistic infections.
• Avoid dental light in patient’s eyes; offer dark glasses for patient comfort.
• Minimize exposure to sunlight and wear sunscreen if sun exposure is planned.
• Ruptures of the shoulder, hand, and Achilles tendons that required surgical repair or resulted in prolonged disability have been reported with this drug.
olanzapine
(Zyprexa, Zyprexa Intramuscular, Zyprexa Zydis)
Do not confuse olanzapine with olsalazine, or Zyprexa with Zyrtec.
Drug Class:
Serious Reactions
! Rare reactions include seizures and neuroleptic malignant syndrome, a potentially fatal syndrome characterized by hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, irregular pulse or B/P, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac arrhythmias.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort because of GI effects of drug.
• Assess salivary flow as factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min before standing to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
• Patients on chronic drug therapy may rarely have symptoms of blood dyscrasias, which can include infection, bleeding, and poor healing.
• Assess for presence of extrapyramidal motor symptoms, such as tardive dyskinesia and akathisia. Extrapyramidal motor activity may complicate dental treatment.
Consultations:
• In a patient with symptoms of blood dyscrasias, request a medical consultation for blood studies and postpone dental treatment until normal values are reestablished.
• Medical consultation may be required to assess disease control.
• Physician should be informed if significant xerostomic side effects occur (e.g., increased caries, sore tongue, problems eating or swallowing, difficulty wearing prosthesis) so that a medication change can be considered.
Drug Class:
Antihypertensive, angiotensin (AT) II receptor blocker.
Serious Reactions
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• Avoid or limit dose of vasoconstrictor.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min to avoid dizziness.
• Stress from dental procedure may compromise cardiovascular function; determine patient risk.
Drug Class:
Angiotensin II (ATI) receptor antagonist
Mechanism of Action
Therapeutic Effect: Causes vasodilation, decreases peripheral resistance, and decreases B/P.
Serious Reactions
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• Avoid or limit dose of vasoconstrictor.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort if GI side effects occur.
• Limit use of sodium-containing products, such as saline IV fluids, for patients with a dietary salt restriction.
• Stress from dental procedures may compromise cardiovascular function; determine patient risk.
• Patients with hypertensive disease may be taking more than one drug to control B/P; although not specifically noted for this drug, postural hypotension is always a possibility.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min before standing to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
• Short appointments and a stress-reduction protocol may be required for anxious patients.
• Use precaution if sedation or general anesthesia is required; risk of hypotensive episode.
Drug Class:
Ophthalmic and nasal antihistamine
Precautions and Contraindications
Contraindicated by hypersensitivity to olopatadine or any of its ingredients
Drug Class:
Antiinflammatory, salicylate derivative
Mechanism of Action
A salicylic acid derivative that is converted to mesalamine in the colon by bacterial action.
Blocks prostaglandin production in bowel mucosa.
Therapeutic Effect: Reduces colonic inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease.
Drug Class:
Indications and Dosages
Serious Reactions
Dental Considerations
General:
• Determine why patient is taking the drug.
• Be aware of patient’s disease, its severity, and its frequency, when known.
• Question patient about other medications used for asthma or to prevent bronchoconstriction.
• Avoid drugs that may aggravate asthma.
• Short appointments and a stress-reduction protocol may be required for anxious patients.
• Have patient bring personal short-acting bronchodilator to appointment for use in emergency.
• Acute asthmatic episodes may be precipitated in the dental office. Rapid-acting sympathomimetic inhalants should be available for emergency use. A stress-reduction protocol may be required.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses



 Diarrhea
Diarrhea Carcinoid Tumors
Carcinoid Tumors VIPomas
VIPomas Esophageal Varices
Esophageal Varices Acromegaly
Acromegaly
 UTIs
UTIs Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Lower Respiratory Tract, Skin and Skin-Structure Infections
Lower Respiratory Tract, Skin and Skin-Structure Infections Prostatitis, Sexually Transmitted Diseases (Cervicitis, Urethritis)
Prostatitis, Sexually Transmitted Diseases (Cervicitis, Urethritis) Prostatitis
Prostatitis Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Sexually Transmitted Diseases Acute, Uncomplicated Gonorrhea
Acute, Uncomplicated Gonorrhea Usual Elderly Dosage
Usual Elderly Dosage Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Bacterial Conjunctivitis Corneal Ulcers
Corneal Ulcers Acute Otitis Media
Acute Otitis Media Otitis Externa
Otitis Externa Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage in Renal Impairment
 Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia Bipolar Mania
Bipolar Mania Dosage for Elderly or Debilitated Patients and Those Predisposed to Hypotensive Reactions
Dosage for Elderly or Debilitated Patients and Those Predisposed to Hypotensive Reactions Control Agitation in Schizophrenic or Bipolar Patients
Control Agitation in Schizophrenic or Bipolar Patients
 Hypertension (with or without Other Antihypertensive Agents)
Hypertension (with or without Other Antihypertensive Agents) Hypertension
Hypertension Allergic Conjunctivitis
Allergic Conjunctivitis Maintenance of Controlled Ulcerative Colitis
Maintenance of Controlled Ulcerative Colitis
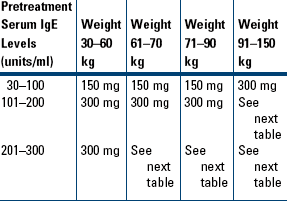
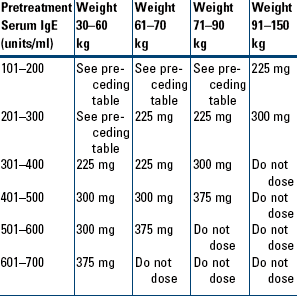
 Moderate-to-Severe Persistent Asthma in Patients Who Are Reactive to a Perennial Allergen and Whose Asthma Symptoms Have Been Inadequately Controlled with Inhaled Corticosteroids
Moderate-to-Severe Persistent Asthma in Patients Who Are Reactive to a Perennial Allergen and Whose Asthma Symptoms Have Been Inadequately Controlled with Inhaled Corticosteroids