Oblique lateral radiography
Introduction
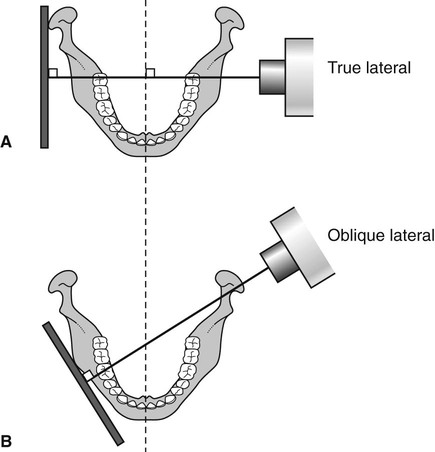
Oblique lateral radiographs are extraoral views of the jaws that can be taken using a dental X-ray set (see Fig. 12.1). Before the development of panoramic equipment they were the routine extraoral radiographs used both in hospitals and in general practice. In recent years, their popularity has waned, but the limitations of panoramic radiographs (see Ch. 15) have ensured that oblique lateral radiographs still have an important role.
Main indications
The main clinical indications for oblique lateral radiographs include:
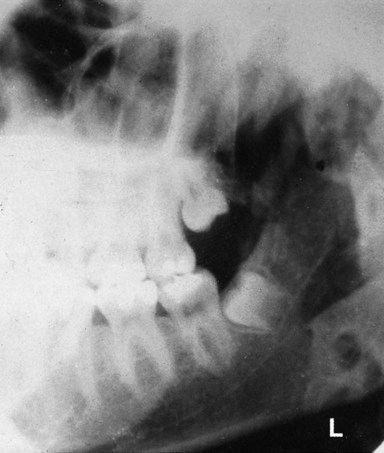
• Assessment of the presence and/or position of unerupted teeth
• Detection of fractures of the mandible
• Evaluation of lesions or conditions affecting the jaws including cysts, tumours, giant cell lesions, and other bone lesions
• As an alternative when intraoral views are unobtainable because of severe gagging or if the patient is unable to open the mouth or is unconscious (see Ch. 8, Fig. 8.1)
• As specific views of the salivary glands or temporomandibular joints.
Equipment required
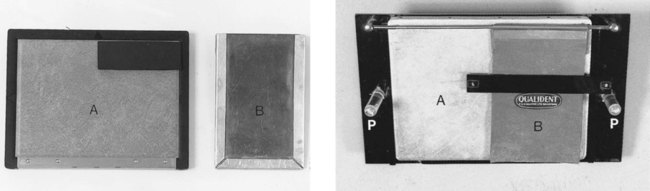
This includes (see Fig. 12.3):
• An extraoral cassette containing film and intensifying screens or a digital phosphor plate (usually 13 × 18 cm)
• A lead shield to cover half the cassette when taking bimolar views.
Specially constructed angle boards, as shown in Fig. 12.3B, can be used to facilitate positioning, but are not considered necessary by the authors.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses