L
Drug Class:
Nonselective adrenergic β-blocker and selective α1-blocker; antihypertensive
Serious Reactions
! Labetalol administration may precipitate or aggravate CHF because of decreased myocardial stimulation.
! Abrupt withdrawal may precipitate ischemic heart disease, producing sweating, palpitations, headache, and tremors.
! May mask signs and symptoms of acute hypoglycemia (tachycardia, B/P changes) in patients with diabetes.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Monitor vital signs at every appointment because of cardiovascular side effects.
• Patients on chronic drug therapy may rarely have symptoms of blood dyscrasias, which can include infection, bleeding, and poor healing.
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Limit dose of vasoconstrictors, or avoid use of vasoconstriction.
• After supine positioning, have patient sit upright for at least 2 min before standing to avoid orthostatic hypotension.
• Limit use of sodium-containing products, such as saline IV fluids, for patients with a dietary salt restriction.
• Stress from dental procedures may compromise cardiovascular function; determine patient risk.
• Short appointments and a stress-reduction protocol may be required for anxious patients.
Serious Reactions
Dental Considerations
General:
• Assess salivary flow as a factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Morning appointments and stress-reduction protocol may be needed for anxious patients.
• Be prepared to manage seizures and/or nausea.
• After supine positioning, allow patient to sit upright for 2 minutes to avoid occurrence of dizziness.
Drug Class:
Antiviral, nucleoside analogue
Mechanism of Action
Therapeutic Effect: Interrupts HIV replication, slowing the progression of HIV infection.
Indications and Dosages
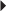 Chronic Hepatitis B
Chronic Hepatitis B
PO
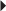 Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage in Renal Impairment
Dosage and frequency are modified on the basis of creatinine clearance.
| Creatinine Clearance | Dosage |
| 50 ml/min or higher | 150 mg twice a day |
| 30–49 ml/min | 150 mg once a day |
| 15–29 ml/min | 150 mg first dose, then |
| 100 mg once a day | 5–14 ml/min |
| 150 mg first dose, then | 50 mg once a day |
| Less than 5 ml/min | 50 mg first dose, then 25 mg once a day |
Serious Reactions
Drug Class:
Indications and Dosages
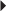 Seizure Control in Patients Receiving Enzyme-Inducing Antiepileptic Drug (EIAEDS), But Not Valproic Acid
Seizure Control in Patients Receiving Enzyme-Inducing Antiepileptic Drug (EIAEDS), But Not Valproic Acid
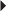 Seizure Control in Patients Receiving Combination Therapy of EIAEDS and Valproic Acid
Seizure Control in Patients Receiving Combination Therapy of EIAEDS and Valproic Acid
 Conversion to Monotherapy for Patients Receiving Valproic Acid
Conversion to Monotherapy for Patients Receiving Valproic Acid
Serious Reactions
! Abrupt withdrawal may increase seizure frequency.
! Serious rashes, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, requiring hospitalization and discontinuation of treatment have been reported.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Morning appointments and a stress-reduction protocol may be required for anxious patients.
• Determine type of epilepsy, seizure frequency, and quality of seizure control.
• Evaluate respiration characteristics and rate.
• Assess salivary flow as factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
• Patients on chronic drug therapy may rarely have symptoms of blood dyscrasias, which can include infection, bleeding, and poor healing.
Drug Class:
Uses
For long-term treatment of acromegaly in patients who fail to respond to surgery and radiotherapy.
Precautions and Contraindications
There are no contraindications listed in the manufacturer’s labeling.
Serious Reactions
! Bradycardia, hypo- and hyperglycemia, gallstones, decreases in thyroid function, renal impairment, and hepatic impairment have occurred.
Drug Class:
Serious Reactions
Dental Considerations
General:
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort because of GI effects of disease.
• Question the patient about tolerance of NSAIDs or aspirin related to GI problem.
• Patients with GERD may have oral symptoms, including burning mouth, secondary candidiasis, and oral signs of dental erosion.
• Assess salivary flow as factor in caries, periodontal disease, and candidiasis.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


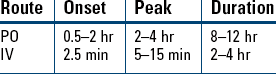
 Hypertension
Hypertension Severe Hypertension, Hypertensive Emergency
Severe Hypertension, Hypertensive Emergency
 Partial-Onset Seizures
Partial-Onset Seizures HIV Infection (in Combination with Other Antiretrovirals)
HIV Infection (in Combination with Other Antiretrovirals)

 Conversion to Monotherapy for Patients Receiving EIAED
Conversion to Monotherapy for Patients Receiving EIAED Bipolar Disorder in Patients Receiving EIAED
Bipolar Disorder in Patients Receiving EIAED Bipolar Disorder in Patients Receiving Valproic Acid
Bipolar Disorder in Patients Receiving Valproic Acid Discontinuation Therapy
Discontinuation Therapy
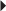 Duodenal Ulcer
Duodenal Ulcer Erosive Esophagitis
Erosive Esophagitis Gastric Ulcer
Gastric Ulcer NSAID Gastric Ulcer
NSAID Gastric Ulcer
 Healed Duodenal Ulcer, GERD
Healed Duodenal Ulcer, GERD Usual Pediatric Dosage
Usual Pediatric Dosage Helicobacter pylori Infection
Helicobacter pylori Infection Pathologic Hypersecretory Conditions (Including Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome)
Pathologic Hypersecretory Conditions (Including Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome)
 Reduce Serum Phosphate in End-Stage Renal Disease
Reduce Serum Phosphate in End-Stage Renal Disease