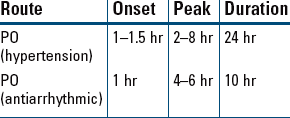
A
Drug Class:
Antiviral, nucleoside analogue
Serious Reactions
! A hypersensitivity reaction may be life threatening. Signs and symptoms include fever, rash, fatigue, intractable nausea and vomiting, severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, cough, pharyngitis, and dyspnea.
Dental Considerations
General:
• Examine for oral manifestation of opportunistic infection.
• Patient on chronic drug therapy may rarely have symptoms of blood dyscrasias, which include infection, bleeding, and poor healing.
• Avoid dental light in patient’s eyes; offer dark glasses for patient comfort.
• Place on frequent recall because of oral side effects.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort if GI side effects occur.
Drug Class:
Serious Reactions
! Immediate-onset systemic allergic reaction characterized by hypotension, urticaria, pruritus, periorbital and/or circumoral edema, shortness of breath, wheezing, and syncope may occur.
! Prolongation of the QT interval may occur. Tightening of throat, tongue swelling, wheezing, shortness of breath, and low blood pressure occur rarely.
Drug Class:
Antirheumatic, disease modifying
Indications and Dosages
 Rheumatoid Arthritis (moderate to severe) in patients who have had an inadequate response to one or more disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs
Rheumatoid Arthritis (moderate to severe) in patients who have had an inadequate response to one or more disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs
Precautions and Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to abatacept or any component of the formulation.
Serious Reactions
! Infections: should be cautious when considering the use of abatacept in patients with a history of recurrent infection, underlying conditions that may increase risks of infections, or chronic, localized infections. These patients should be monitored closely. If a patient develops a serious infection, the treatment should be discontinued.
Drug Class:
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitor
Serious Reactions
! Major bleeding complications may occur. If complications occur, stop the infusion immediately.
! Hypersensitivity reaction may occur.
! Atrial fibrillation or flutter, pulmonary edema, and complete atrioventricular block occur occasionally.
Dental Considerations
Teach Patient/Family to:
• Encourage effective oral hygiene to prevent soft tissue inflammation.
• Prevent trauma when using oral hygiene aids.
• Report oral lesions, soreness, or bleeding to dentist.
• Update health and medication history if physician makes any changes in evaluation or drug regimens; include OTC, herbal, and nonherbal remedies in the update.
Drug Class:
Side Effects/Adverse Reactions
CNS: Headache, somnolence, decreased libido, amnesia, abnormal thinking, tremor
CV: Palpitation, syncope, vasodilation, changes in B/P
GI: Vomiting, dyspepsia, constipation, increased appetite
RESP: Rhinitis, cough, dyspnea, pharyngitis, bronchitis
EENT: Abnormal vision, taste alterations
SYST: Back pain, infection, flu syndrome, chest pain, chills, attempts at suicide (see Precautions)
Drug Interactions of Concern to Dentistry
Dental Considerations
General:
Drug Class:
Serious Reactions
Dental Considerations
General:
• Ensure that patient is following prescribed diet and takes medication regularly.
• Type 2 patients may also be using insulin. If symptomatic hypoglycemia occurs while taking this drug, use dextrose rather than sucrose because of interference with sucrose metabolism.
• Place on frequent recall to evaluate healing response.
• Patients with diabetes may be more susceptible to infection and have delayed wound healing.
• Question the patient about self-monitoring the drug’s antidiabetic effect.
• Consider semisupine chair position for patient comfort if GI side effects occur.
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


 HIV Infection (in combination with other antiretrovirals)
HIV Infection (in combination with other antiretrovirals)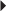 Dosage in Hepatic Impairment
Dosage in Hepatic Impairment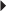 Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer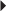 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (moderate to severe), active, polyarticular
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (moderate to severe), active, polyarticular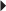 Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (moderate to severe), active, polyarticular
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (moderate to severe), active, polyarticular Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) PCI (unstable angina)
PCI (unstable angina) Dental Use
Dental Use Maintenance of Alcohol Abstinence
Maintenance of Alcohol Abstinence
 Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes Mellitus