2
An introduction to facial growth and development
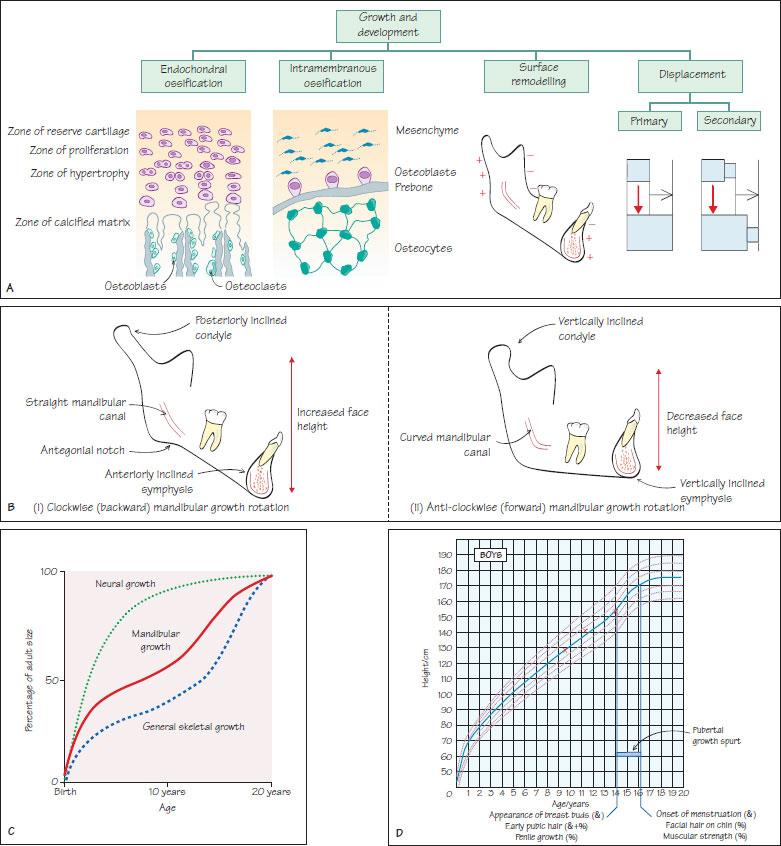
Figure 2.1 (A) The four main processes involved in growth and development of the craniofacial complex. (B) Various cephalometric features can indicate the likely direction of mandibular growth rotation. These features include the lower anterior face height, the shape of the lower border of the mandible, the inclination of the mental symphysis, inclination of the condylar head and curvature of the mandibular canal. (C) The general pattern of skeletal and neural growth is illustrated (Scammons curves). Mandibular growth has some similarity to the general skeletal growth pattern. (D) This figure shows the height curve for males. The average growth curve (50th centile) as well as curves between the 3rd and 97th centile are shown. The pubertal growth spurt is marked as well as the secondary sexual characteristics that may be present at the beginning and end of the spurt. At least three consecutive measurements (red crosses) are required to estimate with reasonable accuracy the growth curve any particular patient maybe following.
Facial growth and development is a complex three-dimensional process occurring until the late teens and then to a small extent in adulthood. Growth refers to an increase in tissue size as a result of cellular hypertrophy, hyperplasia, an increase in extracellular volume or a combination of these factors. Development refers to an increase in tissue organisation and specialisation. It is essential that the reader appreciates that there is tremendous individual variation in the timing, magnitude and direction of facial growth.
The importance of understanding facial growth
An understanding of normal facial growth and development is important to an orthodontist for several reasons:
- understanding the aetiology of malocclusion;
- recognition of abnormal growth patterns;
- treatment timing (e.g. functional appliances, orthognathic surgery);
- understanding factors influencing treatment stability.
Components of the skull
The skull can be divided into two main components:
- Neurocranium (cranial vault and cranial base);
- Viscerocranium (facial skeleton).
The neurocranium has an important role in supporting and protecting the brain, and provides a passageway for nerves and blood vessels. The viscerocranium is particularly important for mastication, respiration and supporting the eyes.
Processes involved in sk/>
Stay updated, free dental videos. Join our Telegram channel

VIDEdental - Online dental courses


